The Softmax Function in Neural Network Attention
Why this simple mathematical function powers everything from ChatGPT to image recognition
Let me start with a real-world scenario - You're at a party trying to follow one conversation while dozens of other people talk around you. Your brain doesn't treat every voice equally. It focuses more on the person you're talking to while staying aware of background chatter that might suddenly matter. This is how modern neural networks handle information through attention mechanisms. At the heart of this process sits a math function called softmax.
I was curious to know the nitty gritty of the neural networks which are fundamental to today’s AI. So, I asked all my queries to Claude and here I am sharing my learnings about this function in easiest way possible.
Vectors: What do these numbers represent?
At the heart of any neural network and LLMs lies Vectors that are used to represent all forms of data in a format that machines can understand and process like words and sentences, images and any other complex data.
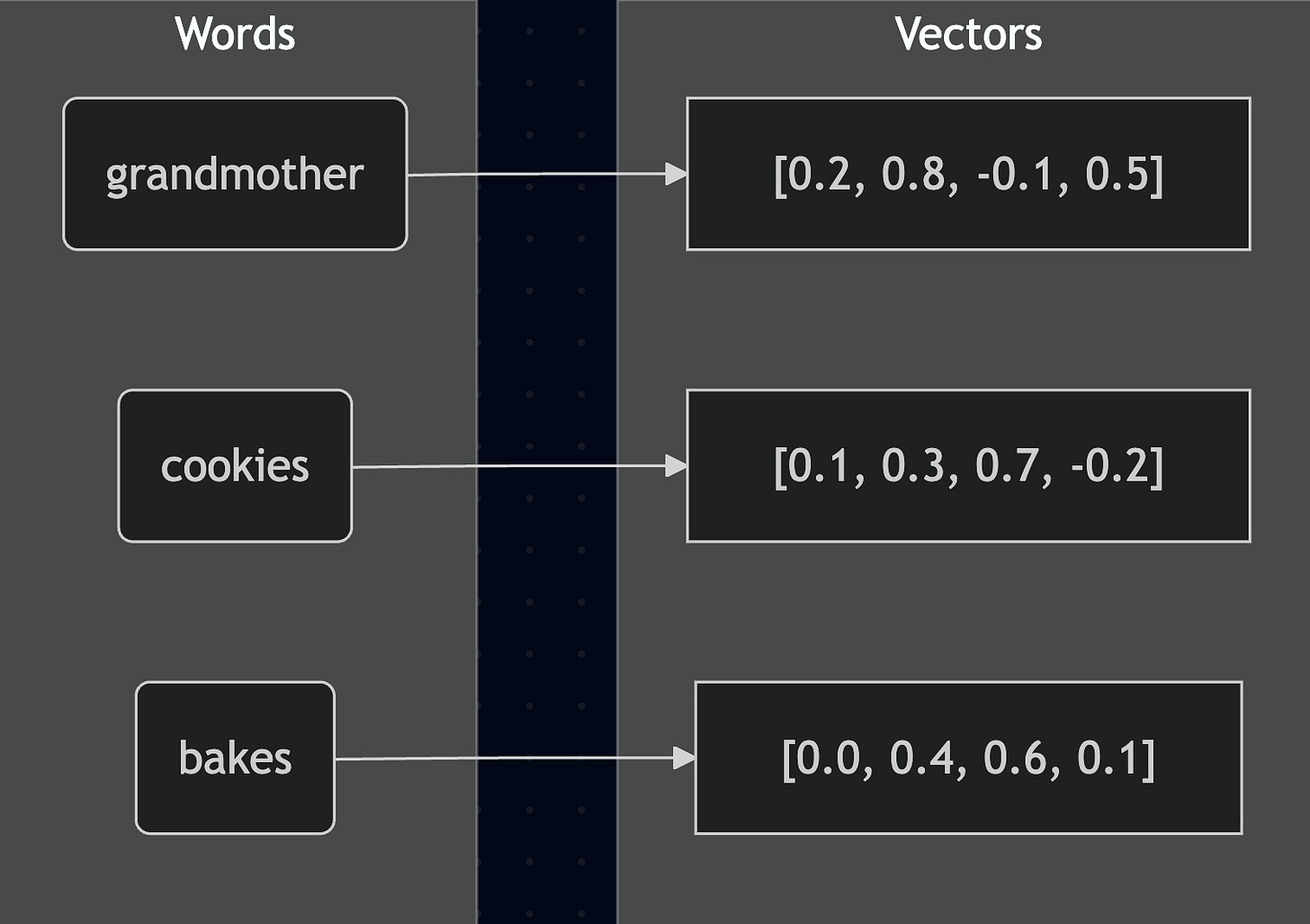
Before we dive into softmax itself, let's understand what those mysterious numbers actually are. When neural networks process text, they don't work with words directly. Instead, they convert each word into a mathematical representation called a vector embedding.
Think of vector embeddings as coordinates that capture the meaning of words in a multi-dimensional space. Just like you might describe a location using latitude and longitude, neural networks describe word meanings using hundreds of numbers. Words with similar meanings end up with similar coordinates.
“My Grandmother bakes incredible cookies”
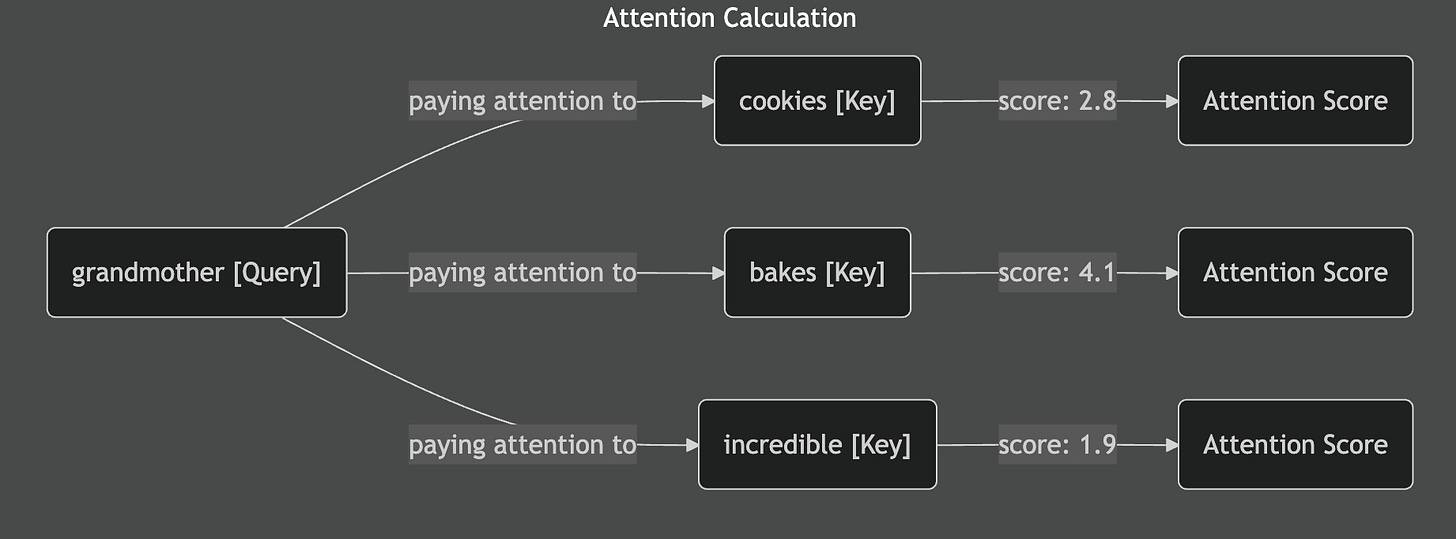
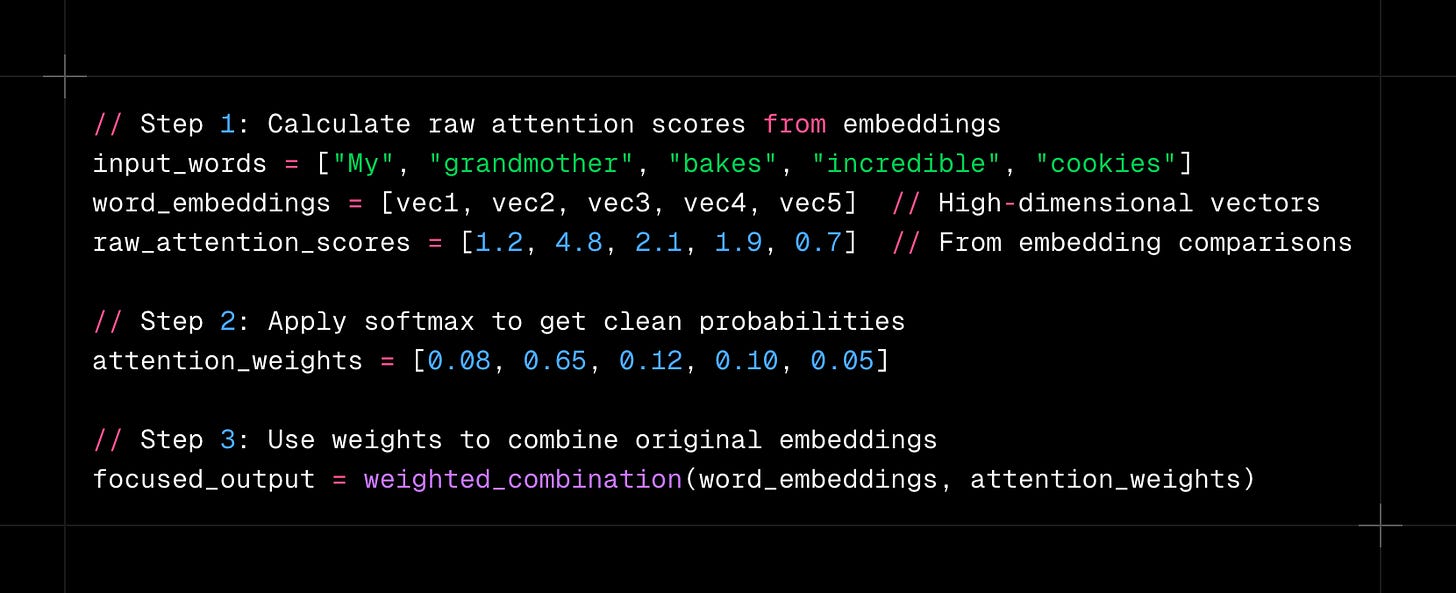
When we calculate attention scores, we're essentially measuring how much each word should "pay attention to" every other word. The network does this by comparing these vector embeddings mathematically. Words that are more relevant to each other get higher attention scores.
These raw attention scores come from mathematical operations between the vector embeddings. They tell us which words are most relevant to each other in the current context. But these raw scores are messy and hard to work with directly, which is exactly where softmax becomes essential.
You might wonder How Words Calculate Relevance to Each Other. I separated that topic to a different article as this one focuses on Softmax. I recommend you read that first before moving ahead with this one.
What Softmax Actually Does
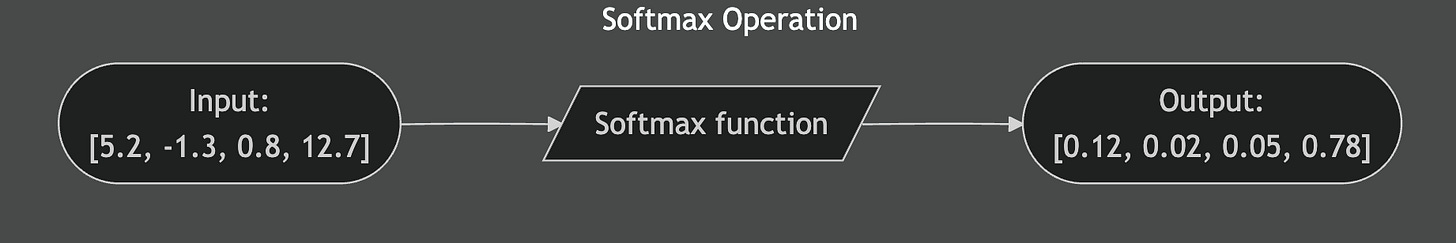
Softmax takes any list of numbers and turns them into probabilities. The input numbers can be anything:
Big, small, positive, negative. The output is always numbers between:
Range: 0 to 1
Sum: Always equals 1Think of it like a voting system. Say three candidates have scores:
The raw numbers are hard to interpret. Is 2.1 much better than 1.8? Softmax converts these into clear percentages. Now you can see candidate A leads but candidate C is still competitive.
Softmax doesn't just scale numbers linearly. It uses exponentials, which means it amplifies differences. If one score is much higher than the others, softmax makes that difference even bigger in the final probabilities. This amplification is exactly what attention mechanisms need.
Here's how softmax works under the hood:
Why Neural Networks Need Attention
Traditional neural networks had a big problem when processing sequences like text. They tried to squeeze all the information from a long sequence into one fixed-size summary. As if you are trying to summarize an entire novel in one sentence. Important details get lost while summarizing.
The core issue was that these networks processed information sequentially, like reading a book from left to right while trying to remember everything. By the time they reached the end of a long sentence, they had often forgotten important details from the beginning. This created a bottleneck that limited their ability to understand complex relationships in text.
Attention mechanisms fixed this by creating a kind of "random access memory" for neural networks. Instead of creating one summary, networks can look back at any part of the input when they need it. When translating "My grandmother bakes incredible cookies" into Spanish, the network can check "grandmother" when generating "abuela" and look at "cookies" when generating "galletas." This selective focus made networks much better at translation, image recognition, and many other tasks.
But implementing this focus required a way to decide which parts of the input matter most at each step. The network needs to assign importance scores to different pieces of information, then use these scores to create weighted combinations. This is where softmax comes in, transforming those raw relevance scores we calculated from vector embeddings into usable attention weights.
How Softmax Powers Attention
Attention mechanisms work in three clear steps, and softmax handles the crucial middle step that makes everything work together.
First, the network calculates raw attention scores between different elements by comparing their vector embeddings. These scores show how relevant each piece of information is right now. The scores can vary wildly and can be positive or negative, depending on how similar or different the embeddings are.
Second, softmax converts these messy raw scores into clean probabilities. All the weights become positive and add up to 1. Since softmax uses exponentials, slightly higher raw scores become much higher probabilities. This creates sharp focus when the network needs it.
Third, these probabilities become weights for combining the original vector embeddings. Elements with higher attention weights contribute more to the final representation. Lower-weighted elements fade into the background, like background conversations at that party.
These weights will multiply the actual vector embeddings to create a focused combination that emphasizes the most relevant information.
This creates "soft attention." Instead of making hard yes-or-no choices about what to focus on, the network blends all available information with different weights. Softmax makes this possible by turning arbitrary scores into meaningful weights.
Other Approaches That Didn't Work As Well
Softmax wasn't the only option researchers tried. Understanding these alternatives shows why softmax became the standard.
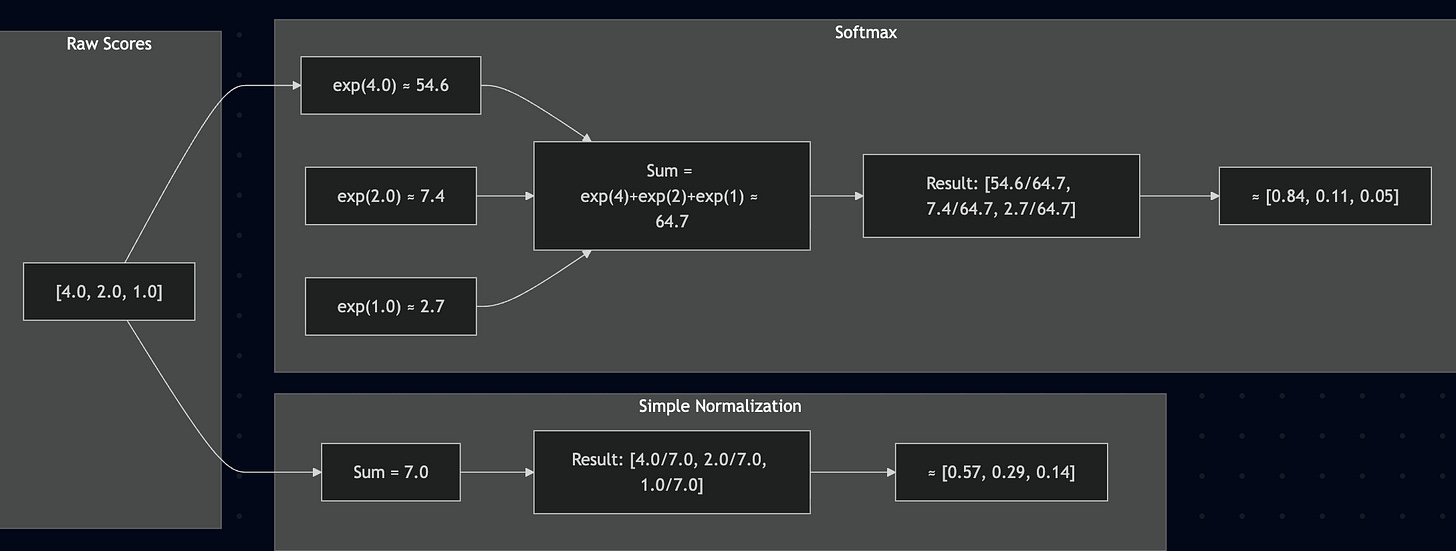
Simple normalization was one alternative. Just divide each raw score by the sum of all scores:
Simple normalization makes weights add up to 1, but notice how softmax amplifies the differences more (Compare - [0.84, 0.11, 0.05] with [0.57, 0.29, 0.14]). The highest score gets even more weight, while the lowest gets even less. This amplification creates the focused attention that works better in practice.
Hard attention was another approach. Instead of weighted combinations, the network makes discrete choices about which elements to focus on. This works well computationally but creates training problems. Discrete choices aren't smooth, which breaks the gradient-based learning that neural networks rely on.
Some researchers tried other activation functions like sigmoid or tanh to convert raw scores into weights. These don't naturally make weights sum to 1, so you need extra normalization steps. They also lack softmax's amplification property, which is crucial for creating focused attention.
Sparse attention mechanisms force most weights to zero, keeping only the highest scores. This can be efficient but often too rigid. Many tasks need to consider multiple pieces of information at once, even when one is clearly most important.
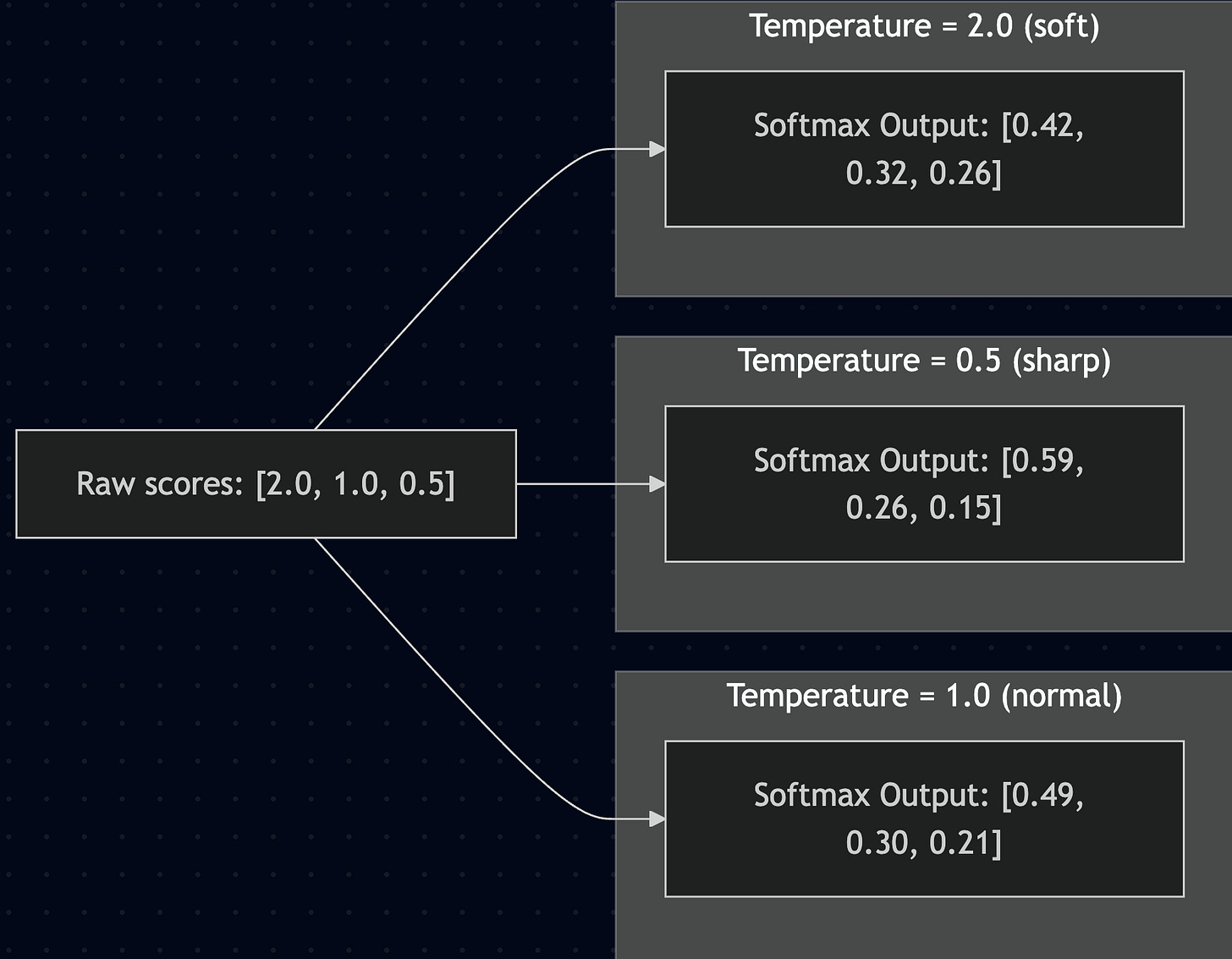
Softmax also has a temperature parameter that researchers sometimes adjust. Here's how temperature affects the same raw scores:
High temperatures create more uniform attention. Low temperatures create sharper, more focused attention. This flexibility lets networks adapt their attention style to different tasks.
Why Softmax Won
Softmax dominates attention mechanisms because it combines several properties that perfectly match what attention needs. It's differentiable, which means gradients flow smoothly during training. The exponential amplification creates natural focus while maintaining awareness of less important elements.
The probabilistic output makes attention patterns easy to understand. When you see these attention weights:
You immediately see the network is focusing heavily on "grandmother" while paying some attention to "bakes" and "incredible" but barely noticing the other words. This interpretability helps with debugging networks and understanding their behavior.
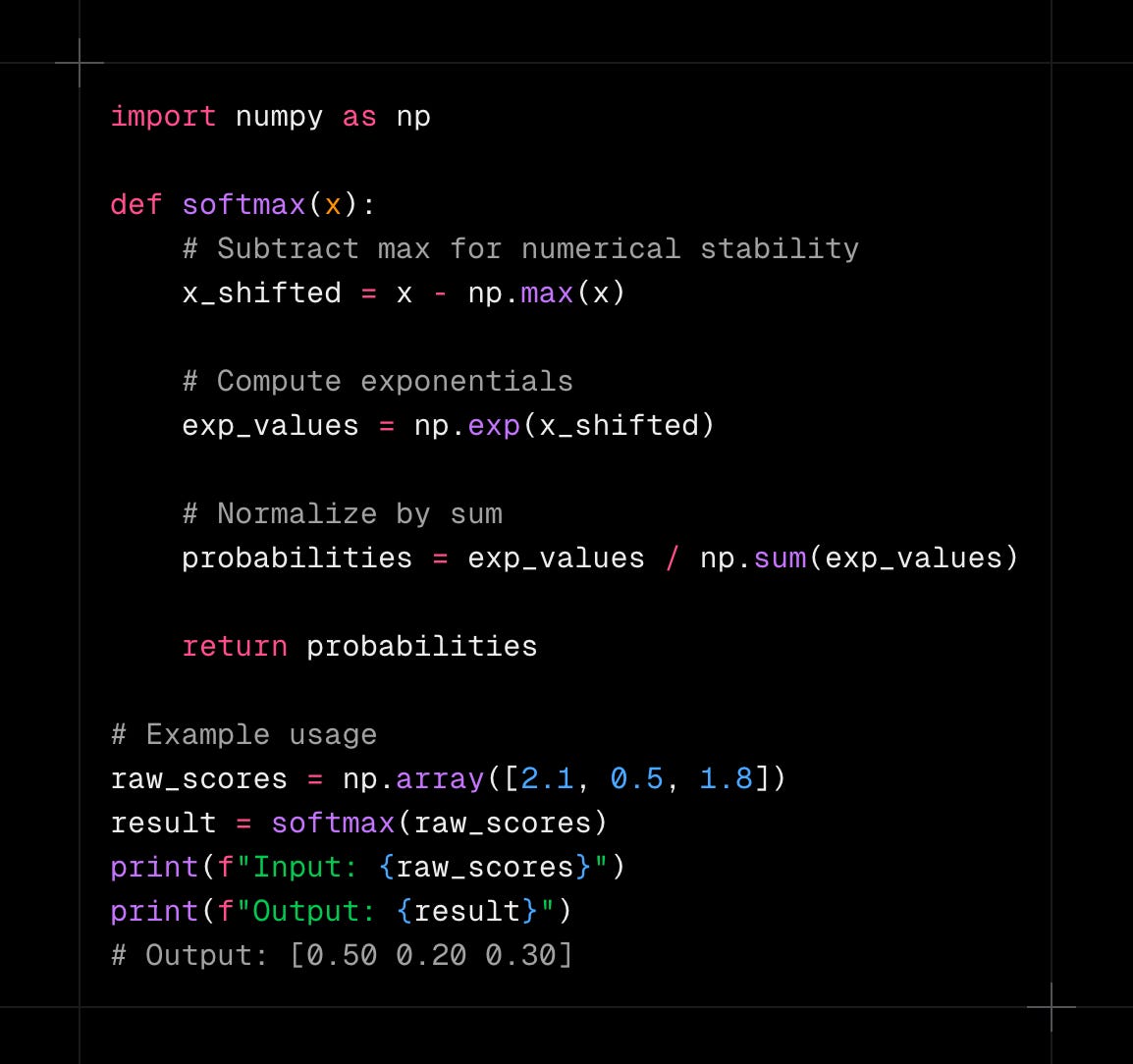
Softmax is also numerically stable when implemented correctly. Modern implementations use mathematical tricks to prevent overflow problems with very large exponentials. This makes softmax reliable in real applications.
The function handles variable-length sequences seamlessly. Whether processing a sentence with 10 words or 100 words.
Softmax creates valid probability distributions without changing the architecture. This flexibility was essential as attention spread from machine translation to computer vision and speech recognition.
How Softmax-Powered Attention Changed AI
The combination of softmax and attention transformed artificial intelligence. The Transformer architecture, built around softmax-based attention, became the foundation for models like BERT and GPT. These models achieved human-level performance on many language tasks.
In computer vision, softmax-powered attention helped networks focus on relevant image regions. This improved object detection, image captioning, and visual question answering. Researchers could also visualize attention patterns to understand how networks process images.
Success in attention mechanisms influenced other areas of machine learning. Researchers started using similar softmax-based weighting in memory networks, recommendation systems, and reinforcement learning. The core insight that exponential amplification creates effective focus while staying differentiable proved useful across many domains.
What's Next for Softmax
Softmax has proven remarkably successful, but researchers keep refining it. Recent work explores adaptive temperature parameters that networks learn to adjust automatically. This creates dynamic attention sharpness based on context. Other researchers investigate alternatives like sparsemax, which can create exactly sparse attention while staying differentiable.
Making softmax computation more efficient has become important as attention scales to longer sequences. Researchers develop approximation methods, specialized hardware, and mathematical optimizations to make softmax-based attention more practical.
Despite ongoing developments, softmax's fundamental role in attention seems secure. Its combination of mathematical elegance, practical effectiveness, and clear interpretability makes it indispensable.
The Right Tool for the Job
Softmax in attention mechanisms shows how the right mathematical tool can unlock major advances in AI. By converting raw attention scores derived from vector embeddings into clean probability distributions while amplifying important differences, softmax gives neural networks the selective focus that makes modern AI systems powerful.
Softmax provides exactly what attention mechanisms need. Its exponential amplification creates sharp focus when necessary. Its probabilistic output makes attention patterns interpretable. While researchers explored many alternatives, none matched softmax's unique combination of mathematical properties and practical effectiveness.
Understanding softmax's role in attention provides insight into one of the most important developments in modern AI. It shows how sophisticated behaviors like human-like selective focus can emerge from elegant mathematical foundations. As neural networks continue evolving, the principles that softmax embodies will likely keep guiding their development.
AI and LLMs in particular is a very interesting field not because it can improve the productivity by 10x or 100x, but the history behind it. The research behind every aspect of this and softmax is just 1 such example.
I have just started the basics of LLMs and everything that made AI work and reach the stage it has become now. I will be sharing more learnings in coming posts in easier language. Subscribe to not miss out.